Abstract
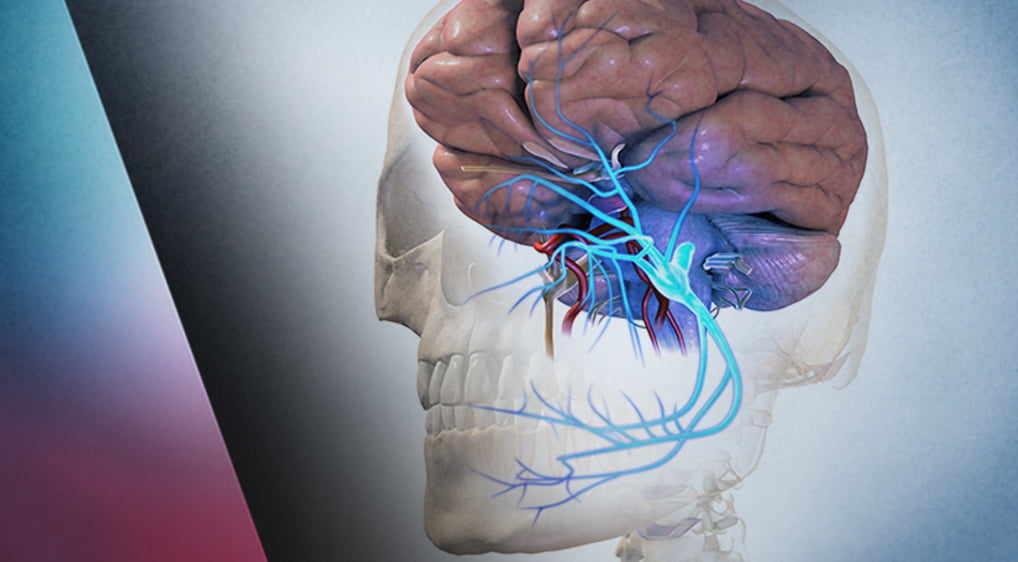
Introduction We report our initial series of patients treated with radiosurgery to the Centromedian (CM) and Parafascicular (Pfc) Complex (CM-Pf) of the contralateral thalamus mainly for trigeminal neuralgia that had failed most known forms of conventional treatments. The coordinates were co-registered to a three-dimensional atlas of the thalamus in order to have a better comprehension of isodose curves distribution. Methods A fully automated rotating gamma ray unit was used to deliver a high dose of radiation (140 Gy) using a 4-mm collimator to the CM-Pf of the contralateral thalamus in 14 patients suffering from refractory trigeminal pain and other complex pain syndromes. The best stereotactic coordinates were plotted in a thalamic three-dimensional atlas space along with isodose curves corresponding to 50% of the dose prescription and the dose gradient. Results From November 2016 to July 2019, 14 patients experiencing severe forms of different pain syndromes were treated, and 10 were eligible for follow-up evaluation. Pain deriving from trigeminal neuralgia was present in the majority (80%) of patients and from other complex pain syndromes in the rest (20%). Median follow-up was 384 days (range: 30-994). The Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) score before treatment was 9 (range: 7-10) and standardized to 10. Before treatment, all the patients had a Barrow Neurological Institute Pain Scale (BNI) of 5 (V). The median years suffering from pain was 4.5 years (range: 1-15), the number of procedures including radiosurgery to the trigeminal nerve before thalamotomy was four (range: 1-10). Most patients (90%) reported some form of relief, the average VAS at the time of response was 3.5 (range: 0-9), and the average time to response was 67.3 days (range: 2-210). The neuromodulation effect of radiation was seen in 60% of patients. The average BNI score at response was 2.7 (range: 1-5). The final VAS score at last follow-up was 5.5 (range: 0-10) in six patients. In four patients (40%), the procedure had failed with a final BNI of IV, and V, three patients (30%) had excellent response (BNI of I), and three patients (30%) had worthwhile results with BNI of IIIa and IIIb. The total success rate (BNI of I to IIIb) was 60%, and the number of patients experiencing more than 50% of pain reduction at final follow-up was five (50%). Excluding both patients that were treated for pain outside of trigeminal neuralgia, 75% of the patients responded. The best coordinates on average were X: 5.5 mm from the thalamic border, Y: 3.7 mm anterior to the posterior commissure, and Z: 3.7 mm from the intercomissural line. There were no complications to report. Conclusion Radiosurgery to the CM-Pf of the thalamus was demonstrated to be a safe and relatively effective alternative to treat refractory trigeminal neuralgia. Further studies are needed to optimize target dimensions based on the three-dimensional studies of isodose curves as well as coordinates. Longer follow-up is necessary to evaluate recurrence rates that could not be reached.
Keywords: functional radiosurgery; neurosurgical management; pain; radiosurgery; thalamotomy; trigeminal neuralgia.
Copyright © 2019, Lovo et al.